The Model View ViewModel (MVVM) is an architectural pattern used in software engineering that originated from Microsoft which specialized in the Presentation Model design pattern. is a software architectural pattern that helps in splitting the GUI code – from the development of the business logic or back-end logic (the model) so that the view is not dependent on any specific model platform.
MVVM Architecture
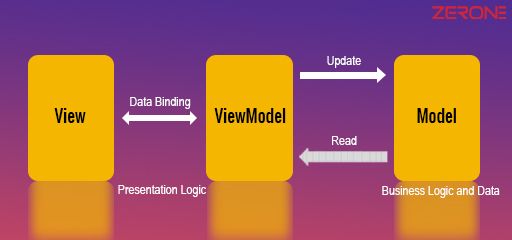
VIEW: View is responsible for front-end look and feels and it doesn’t have any code supporting it. It is bound to the view-model by only using data binding.
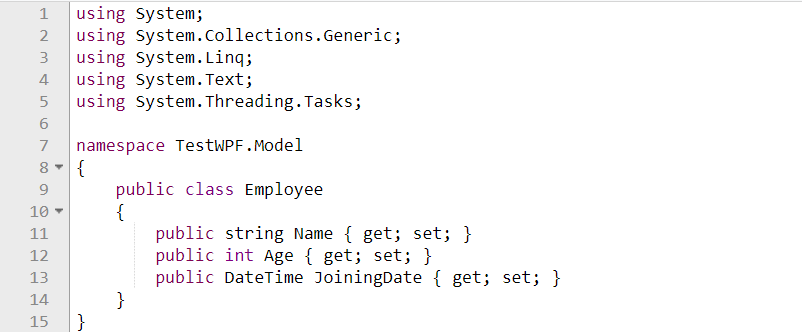
MODEL: Model is the domain object that represents the actual data we are dealing with
VIEWMODEL: It acts as the bridge between the Model and View.
The view binds to properties on a ViewModel, which, in turn, exposes data contained in model objects and other state-specific to the view.
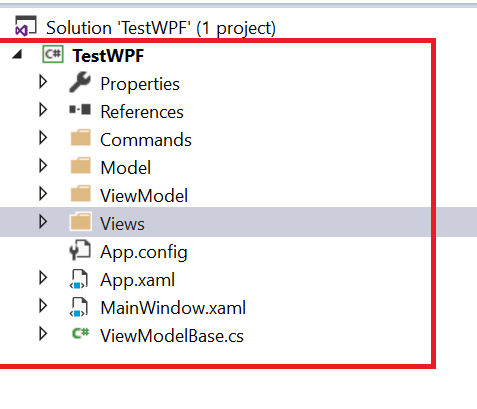
MVVM in Windows Presentation Foundation The Windows Presentation Framework (WPF) can leverage MVVM) pattern to build WPF applications in a much simpler way. Let’s look at a sample Project Architecture shown below:
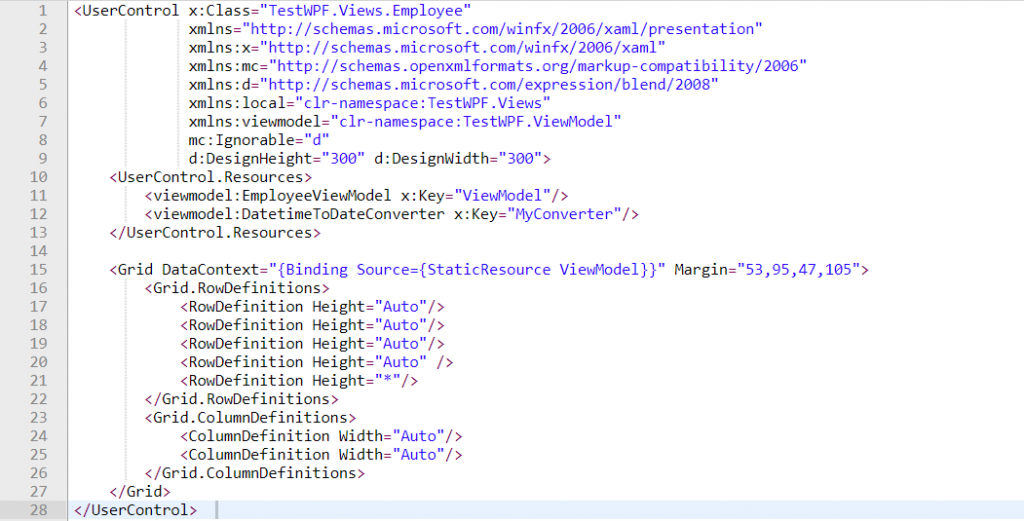
VIEW: It is a visual element, such as a page, user control, window, or data template. It uses the data-binding capabilities of WPF to bind the properties defined in ViewModel to user controls that View is composed of.
User-events that are captured by the View are sent to the ViewModel through Commands. Now, these commands execute methods defined in the ViewModel which contains logic.
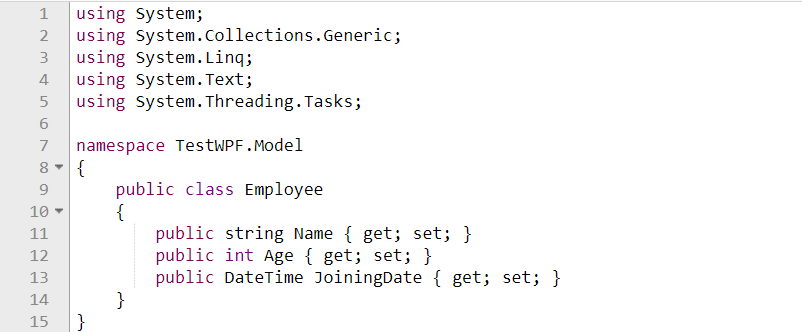
MODEL: Model Class is responsible for data representation. It is used to expose the data objects in an appropriate way that those can be easily managed and consumed by View and ViewModel.
VIEWMODEL ViewModel in the MVVM design pattern encapsulates the presentation logic and data for the view. It simply holds the data retrieved from the data layer. It is never tightly coupled with the View and notifies later, if any property changes in ViewModel. It might take inputs from View and place it on Model, or it might interact with a service to retrieve the model, then translate properties and place it on View. It also exposes methods, commands, and helps to maintain the state of the View, manipulates the Model as the result of actions on the View, and triggers events in View itself. ViewModel always updates Model and properties defined from View having UI level events mapped to commands in ViewModel by two-way data binding.
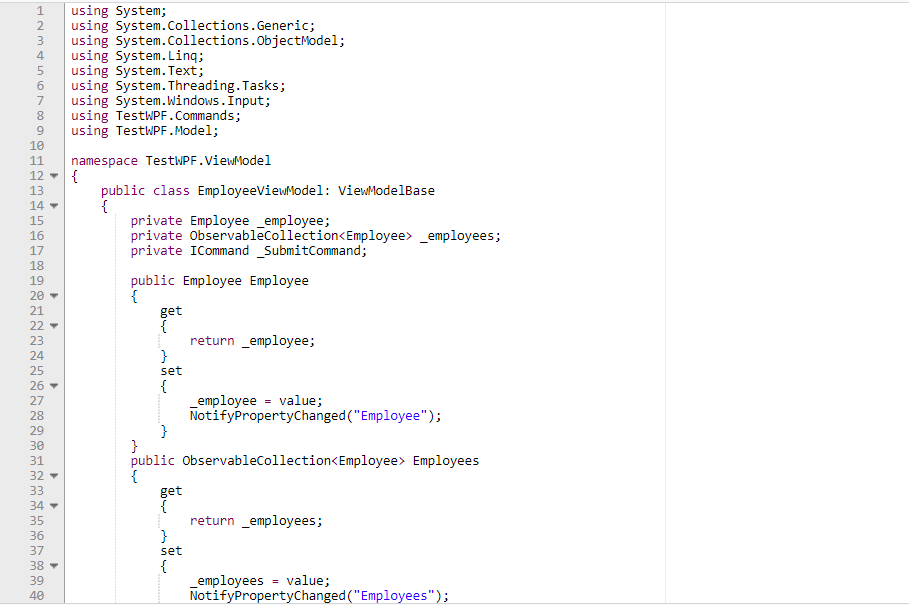
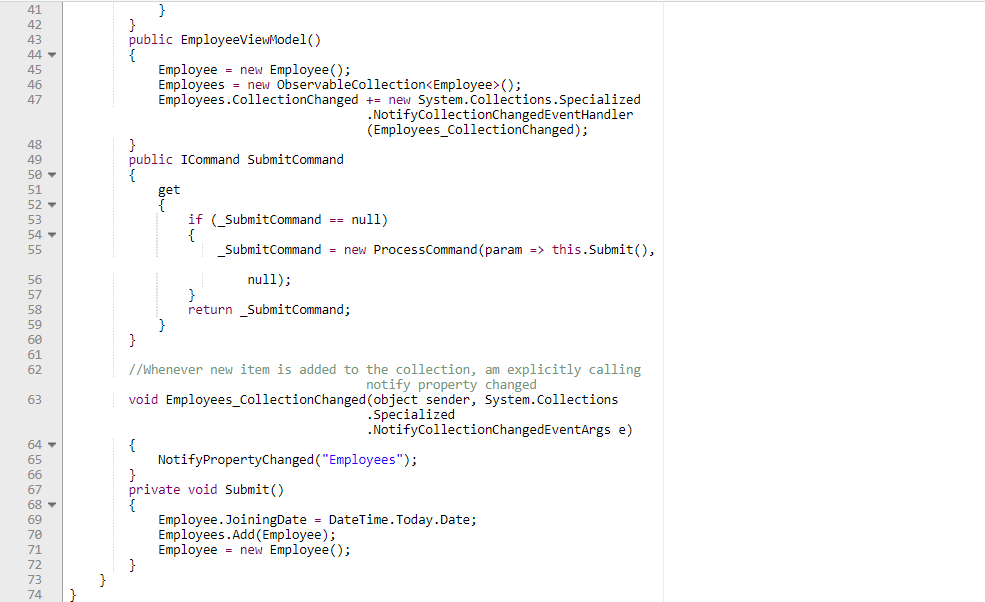
WPF Application using MVVM
The steps for creating a sample WPF application is shown below
- Create a model class Employee
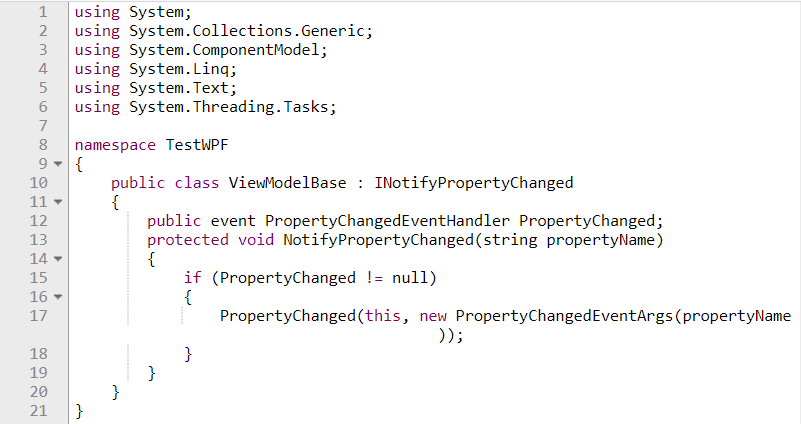
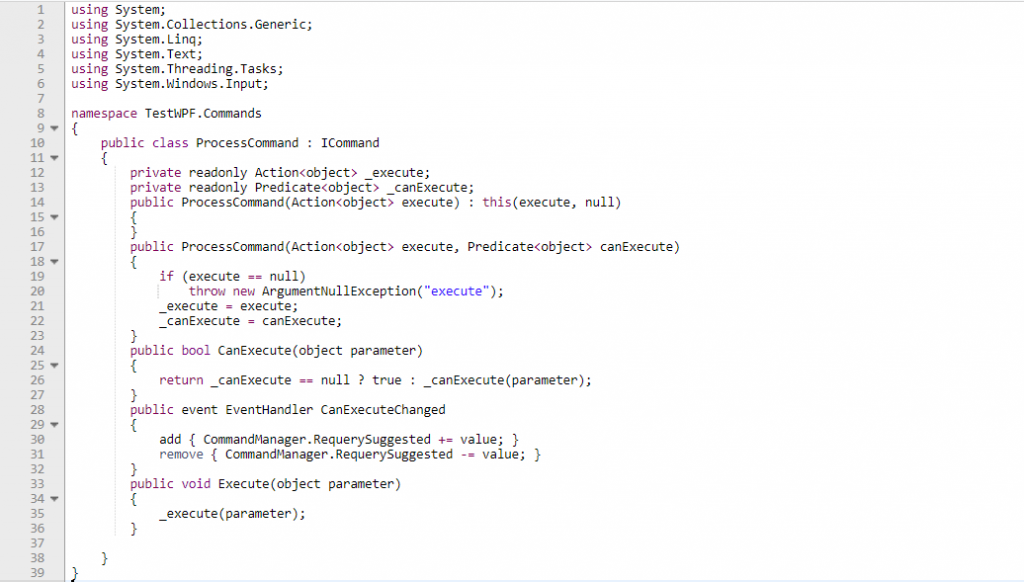
All ViewModel classes are inherited from ViewModelBase. Whenever property changes in View notification will get in ViewModel by implementing INotifyPropertyChanged . This implementation can be done in ViewModelBase and can reuse across all ViewModels which inherits from ViewModelBase,
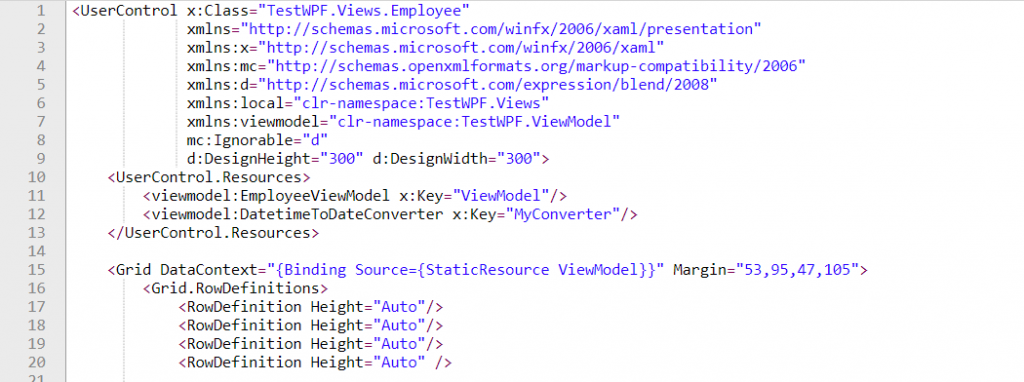

Here we have created User Control and include it in the main view as shown below.
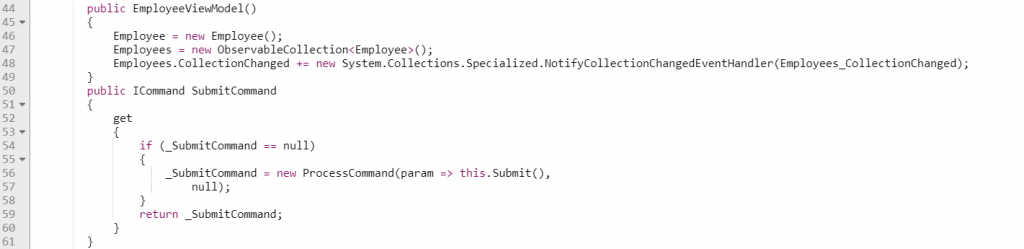
Submit action will trigger submit logic in the Submit method using ‘SubmitCommand’. After submit action Employees property will change with modified employee list and it will notify in view using INotifyPropertyChanged implementation in ViewModelBase


By applying the MVVM pattern in WPF, we can build applications that are more streamlined to improve business application development process. The resulting applications can be maintained effectively and are better for testing as well.