Throughout the history of industrial revolutions, operational and technological changes in manufacturing have always catalyzed industrial and societal transformation forward. Today, as we stand in the midst of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, commonly termed as Industry 4.0, manufacturing is evolving to become a highly connected, intelligent, and productive industry due to the advent of a new generation of sophisticated technologies.
The pandemic has only steered the way forward for manufacturing industries to reimagine their operational processes. According to a recent survey by Decision Analyst, the technologies that bring greater insights and mobility are the key to enabling digital transformation in manufacturing.
What are the technologies that will transform manufacturing in 2020 and beyond? Here, we take a look at three of them.
Incorporating 5G technology:

Let us look at some of the areas in which 5G can add value in the manufacturing sector:
-
Optimizing production cycle: Collecting real-time analytical data on various aspects of production will help manufacturing companies streamline factory activities, maximize output, and reduce waste.
-
Remote connectivity: Enterprise IT systems could be integrated with the infrastructure and operational models, to optimize daily operations.
-
Supply chain integration: Once 5G is integrated into the supply chain, it will be able to rapidly restore parts and supplies that are critical to the manufacturing process, which will decrease delays and increase efficiency.
-
Safety: Interconnected high-speed 5G sensors allows quicker response times to challenges within the manufacturing unit. Consequently, emergency response teams can act quicker and decrease the amount of time and effort wasted in getting things back on track.
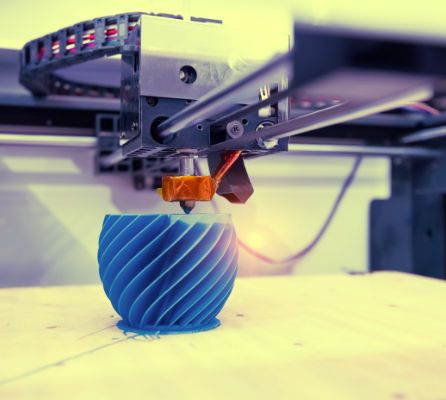
3D printing
The manufacturing industry is always on the lookout for innovative ways of operation. After HP launched their 3Dprinting technology called Metal Jet Technology, for the production of metal parts. This method increases the productivity of the metal manufacturing unit by more than 50x.
Some of the areas in which 3D technology can help in manufacturing are:

-
Lowering cost: 3D printing makes it possible to exponentially increase productivity at significantly lower costs. The increased speed with help in a quicker go-to-market rate. It also uses a lesser amount of manual labor when compared to traditional methods
-
Risk reduction: 3D printing allows manufacturers to confirm the design of the product through 3D prototypes, before moving on to large-scale production. This reduces the risk of errors and streamlines ht over-all process cycle.
-
Consolidating parts: With 3D printing, manufacturers can combine multiple parts into a single entity. This will lead to a decrease in the overall number of parts to assemble and maintain, and increase efficiency
-
Reducing wastage of resources: Since 3D printing is done sequentially in layers, the structure is only created based on need. Those produce less wastage when compared to conventional methods of manufacturing.
Digital Twin Technology
While the digital twin technology has been around for the better part of the decade, the number of manufacturing companies adopting it are less. However, the situation is predicted to change in the next few years. A study by Business Wire predicts that the global digital twin market is projected to grow from $2.66 billion in 2020 to $29.57 billion by 2025. Though COVID-19 has put a slight damper on the growth of the digital twin industry, it is predicted to see a boost by the third quarter of 2020.
Some of the aspects of manufacturing where digital twin technology can add value are:
-
Reduction in costs: Since digital twins are virtual representations fo physical assets that can receive real-time information from the object to understand its performance. With big data and IoT applied to the data, manufacturers can get deep insights into numerous ways to reduce costs and increase performance.
-
Customizing design: Digital twin technology will allow manufacturing companies to virtually model various versions of a product for the customer before it goes into production. It will make it easier to incorporate customer feedback and improve customization.
-
Increase performance: Real-time insights from digital models can help predict the defects present in any manufacturing unit and fix the issue before it disrupts the manufacturing cycle.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Imagine you are heading a company that manufactures Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) units for your consumers. If you are smart enough to invest in IoT, you can remotely monitor and maintain your HVAC system’s performance in your consumers’ homes or offices, detect any failures or leaks and alert your consumers to possible problems. If you are additionally proactive, you can manage, engage, and reassure the customer that the problem can be solved remotely.
Hyperconnectivity, predictive and preventive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and enhanced operational capabilities are some of the benefits that IoT offers to manufacture. The explosive growth of IoT is most commonly discussed in terms of consumer products and devices. However, the technology’s scope in the manufacturing sector and its potential for connectivity throughout the supply chain is wider than consumer IoT applications. In manufacturing, IoT connects assets to processes, systems, and people.
Multiple ways IoT drives efficiency in manufacturing

-
Using intelligent assets and equipment
- Prevent delays in production and improve the performance of the production line
- Reduce equipment downtime and increase process efficiency
- Accelerate equipment repairs
-
Cognitive analytics, processes and operations
- Improve the production line’s productivity through inventory and scrap reductions
- Expedite service calls and repairs, and reduce warranty costs
- Improve quality and yield through enhanced quality practices
-
Smart use of analytics to explore inputs like geolocation data, usage data, individual data, and environmental conditions to:
- Improve worker safety and streamline workforce management
- Increase employee productivity and expertise
- Reduce energy consumption in facilities and buildings
Optimization of resources such as people, energy, or knowledge, is crucial for driving down costs and improving overall engagement and productivity levels.
Artificial Intelligence
A study by Grand View Research predicts that by 2027, the global smart manufacturing market will be well over USD 514.3 billion. Another commonly witnessed trend of AI in manufacturing is that most of the leading companies that build machine learning tools for manufacturing are also using the same tools in-house, into their own manufacturing operations. This makes them the developer and the first customer simultaneously. For instance, the German multinational Siemens has been using neural networks to monitor its steel plants and improve efficiencies for a long time. This practice has made Siemens a leader in developing AI for manufacturing and industrial applications.
AI’s potential in manufacturing

- Ability of AI to adapt to continuously changing tasks, rather than managing the mere traditional repetitive tasks
- Highly beneficial in carrying out predictive maintenance for manufacturing equipment and real-time problem solving through sensors which track the operating conditions and performance
of factory tooling
- Self-learning AI system that learns to predict equipment or tool breakdown and malfunctions, and has the ability to take or recommend corrective actions, which will considerably save costly
manufacturing recalls and repairs
- Integration of AI with big data analytics and cloud will help manufacturers make more informed decisions at each stage in the production process in real-time
- Technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence help us to identify microscopic defects in products, well beyond human vision
- The use of AI in the supply chain enables manufacturing companies to forecast demand patterns for their products across various geographic and socioeconomic segments
The future
The changing customer demands along with the transforming economics of production and distribution are compelling manufacturers to explore more sophisticated and cognitive technologies. Industry 4.0 is not just the adoption of advanced digital technologies in manufacturing, but it rather denotes the holistic transformation in production and supply chain, and the changes brought to traditional production relationships among suppliers, producers, and customers.
“Industry 4.0 is a transformation that makes it possible to gather and analyze data across machines, enabling faster, more flexible, and more efficient processes to produce higher-quality goods at reduced costs. This manufacturing revolution will increase productivity, shift economics, foster industrial growth, and modify the profile of the workforce—ultimately changing the competitiveness of companies and regions.” – Boston Consulting Group.